- Android Revison (Completed): http://www.codelearn.org/android-tutorial#tutorial
- Android Layout (graphical learning) : http://www.raywenderlich.com/78576/android-tutorial-for-beginners-part-2

# IntelliJ Ignore file .idea/ *.iml *.iws out/ *.DS_Store
#The .gitignore for the Android Project developed on Eclipse # Macintosh files .DS_Store # generated files (except .apk) bin/ !bin/*.apk gen/ libs/ # Eclipse project files .classpath .settings .project project.properties # built application files !*.apk # files for the dex VM *.dex # Java class files *.class # Proguard folder generated by Eclipse proguard-project.txt proguard/ lint.xml
//Log Message String msg = "Nitin inside MainActivity: "; Log.e(msg,"Inside BroadCast Intent Method in Main Activity"); //Toast Message Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"Flashing Message", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); Toast.makeText(this,"Flashing Message", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
//sending the intent from mainActivity to TweetListActivity Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, Next_Activity_To_Go.class); startActivity(intent);//Picking up the values from the TextBox which is called EDITTEXT View (R.id.enter_username) in Android. EditText userName = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.enter_username); //Convert into String String userNameValue = userName.getText().toString(); //Check the result in LogCat Log.d("CodeLearn","username cought = " + userNameValue);// For on Click of a LIST @Override protected void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) { /* Picking up the tweetTitle textView and change its value */ //TextView t = (TextView) v.findViewById(R.id.tweetTitle); //t.setText("Tweet Clicked"); //Calling another page (TweetDetail Activity) Intent intent = new Intent(this, TweetDetailActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } /* OnClickListener for a Button */ //Inline findViewById(R.id.button).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClick @Override public void onClick(View v){ Toast.makeText(this, "Button Clicked :)", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT); } });public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); /*setContentView is called withthe constant at * R.layout.main to set the layoutcdefined in main.xml on the screen */ setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); }@Override public void onClick(View v) { // Launch Activity Two // Hint: use Context's startActivity() method // Create an intent stating which Activity you would like to // start Intent intent = null; intent = new Intent(ActivityOne.this, ActivityTwo.class); // Launch the Activity using the intent startActivity(intent); //in one Line startActivity(new Intent(ActivityOne.this, ActivityTwo.class)); }
Collections (DurgaSoft Notes)
Arrays and ArrayList (Strengths and Limitations)
Object[] o = new Object[1000]; //FIXED SIZE!!
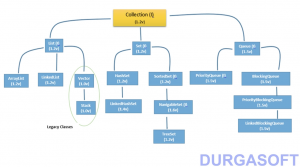
All Above keeps groups of objects. For Key value pairs, Maps(I) is used. (Not in Collection Framework)
Cursors in Java
Sorting
Utility Classes
Constructors
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();new capacity = current capacity * (3/2) + 10
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(int initial_capacity)ArrayList al = new ArrayList(Collection c)Only ArrayList and Vector classes implements RandomAccess Interface (java.util) (so that any random element can be accessed in same time/speed). RandomAccess doesn’t contain any method. Its a Marker Interface
Thus if frequent operation is RETRIEVAL, ArrayList is the best choice. For add, remove, its worst(lost of shifting if addition is done in the middle of ArrayList)
| ArrayList | Vector |
| all methods are non-synchronized | most of the methods are synchronized |
| Not thread safe | Thread safe (Only one thread can access) |
| Performance is relatively high | Relatively Low Performance |
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();//non Synchronized
List l = Collections.synchronizedList(al);
public static List synchronizedList(List l)
public static Set synchronizedSet(Set s)
public static MAp synchronizedMap(Map m)
Methods (Only for Linked List)
vector specific methods (long method name, the burden of Legacy class)
Enumeration e = v.elements
**(v is vector, Only for Legacy Class)
**Has only two methods—boolean hasMoreElements(); & Object nextElement();(type casting is required)
Iterator itr = c.iterator();
Where c is any collection object
Methods:
Example : Program to remove odd elements from an ArrayList
ArrayList l =new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
l.add(i);
}
Iterator itr = l.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()){
Integer n = (Integer)itr.next();//type casting is required as next() returns an Object type
if(n%2 != 0)
itr.remove();
}//end While
Limitation of Iterator
Methods:(9 in total)
ONLY APPLICABLE FOR LIST OBJECTS
Enumeration e = v.elements();
System.out.println(e.getClass().getName());//Vector $1 -> $ = inner class, 1 anonymous inner class
Constructor
Specific methods
Constructor
TreeSet Details
class testComparator implements Comparator{
public int compare(Object obj1, Object obj2){ //provide
Integer i1 = (Integer) obj1;//type casting to be sure of int
Integer i2 = (Integer) obj2;
//For Strings
/*String s1 = (String) obj1;//Type casting
String s2 = obj1.toString();
return -s1.compareTo(s2);//Reverse alphabetical order
return s2.compareTo(s1);//Also Reverse sorted
*/
//For decreasing order, return -ve when obj1 > obj2
if (i1 > i2)
return -1;
else if (i1 < i2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Tweek
return i1.compatrTo(i2);// Ascending order
return i2.compareTo(i1);// Decreasing order
return -i1.compareTo(i2);// Decreasing Order
return 1; // Insertion order
return -1; //reverse insertion order
return 0; //only first element is inserted and all other are considered as duplicates
}
TreeSet t = new TreeSet(new testComparator);
t.add(100); t.add(20);
| Comparable | Compartator |
| java.lang (for DNSO) | java.util (Customised) |
| one method compareTo() | two mwthods compare() and equals() |
| All Wrapper + String Implements it | Collator and RuleBasedCollator (only two classes) |
ArrayList l = new ArrayList();
l.add("Nitin");
//String s = l.get(0);// incompatible type found exception
String s = (String) l.get(0);
int[] nums => nums.length; String str => str.length(); ArrayList<Integer> a => a.size();
return (a > b && (a-b) >= 2);
is equivalent to
if (a > b && (a-b) >= 2){
return true;
}int[] a; a = new int[3]; //notice []. NOT () to be usedint[] a = new int[3]; //single line declarationa.length ; //Length is a "field" in Array, while a method in Stringsint[] a = new int[] {1,2,3};int[] b = {1,2,3};Import java.util.ArrayList;
ArrayList<Integer> b = new ArrayList<Integer>;Arrays.toString(a);//o/p [1,2,3]Arrays.asList(a);Arrays.asList.contains("a");//boolean true/false+ ⇒ concatenationstr.chatAt(i);str.length(); //Method in String, Field in Arrays;str.substring(i,j);//j not includedstr.substring(i);//from i till end str.substring(i,str.length());String Index begins from ZERO, thus lenght = max Index + 1For Equality str.equals();//DO NOT USE == (will compare objects)str.indexOf("er");//2 if "er" begins from index 1, -1 if not Foundstr.indexOf("er", 2); //start the search from index 2str.lastIndexOf("ew");//searches right to leftstr.lastIndexOf("ew", 5);//right to left, from index 5
str.toLowerCase() / str.toUpperCase()str.compareTo("");str.replace("old","new");String[] ransomWords = ransom.split(" ");//Cut the Strings from spaces into a wordsimport java.util.Scanner;Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);int n = in.nextLine();in.nextLine(); //To avoid INPUT ProblemString str = in.nextLine();
/* Input Problem occurs when a mix of int and strings are givenThe extra invocation is done to get rid of previous \n 16\n 1000\n Joe\n /n Extra in.nextLine()
in.nextInt; //reads next integerin.nextDouble();in.nextLine();//reads entire line of inin.next();//next character upto but not including space
/* NO METHOD TO READ A SINGLE CHARACTER */char a = in.nextLine.charAt(0);
//Open the FileFile myFile = new File("/nitin/a.txt");Scanner in = new Scanner(myFile; //Instead of System.in, take the file to read
//Read from the FileString str = in.nextLine();
//ORwhile (in.hasNext());System.out.println(in.nextLine());//Close the Filein.close();
import java.io.PrintWriter;final String FILENAME = "nitin.txt"; //Surrounding with try catch!! ORPrintWriter output = new PrintWriter(FILENAME);
PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter("nitin.txt");
output.println("Nitin");output.println("Chaurasia");
//To avoid erasing files that already existPrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("nitin.txt", true));
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("Names.txt", true);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
OR
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("Names.txt, true"));
File myFile = new File("customer.txt");
Scanner ipFile = new Scanner(myFile); //instead of System.in
/*Assuming 2 command line arguments <Nitin 29>*/
if (args.length == 0 || args.length > 2) {System.err.println("Incorrect Number of arguments passed");System.exit(-1);}
String name = args[0];int age = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
System.currentTimeMillis();//type long , from Jan 1 1970System.nanoTime();
import java.util.Random
Random generator = new Random(); //or new Random(123), 123 being the seed
generator.nextInt(5);//range 0 to 5, add 1 to get range 1 to 6 (dices)
generator.nextInt(); // 2^31 to 2^31 -1
generator.nextDouble();//Range: 0.0 to 1.1
Eg: int throw = generator.nextInt(6) + 1;

for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){ System.out.prinln(arr[i]); } for (ListNode runner = head; runner != null; runner = runner.next){ System.out.println(runner.data); }
LinkNode runner = front;//head
while (runner.next != null){//Runner stops at the last node, else runner will end up pointing null!!
runner = runner.next; front = new ListNode(value, front);
if (index == 0)
front = new ListNode(value, front);
else{
ListNode runner = front;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++)//Stop at an index one before the desired
current = current.next;
}
current.next = new ListNode(value, current.next); //old current.next is assigned to the new node which in turn is assigned to current.next
if (front == null)
front = new ListNode(value, front);
else{
ListNode runner = front;
while (runner.next != null) // Go till the last node
runner = runner.next;
runner.next = new ListNode(value); //this constructor has .next as null
}
for (type name : collection){}
Eg: Set<Double> grades = new HashSet<Double>();for (double g: grades){System.out.println(g);}
Iterator itr = c.iterator();itr.remove(i);itr.hasNext();itr.next();
a = a^b;
b = a^b; //a^b^b yields a
a = a^b;//a^b^a = b(b is recently converted to a)
The logic is used for finding a unique element among duplicates (Stolen Drone problem (21) in Interview cake)
if (flag2 ^ flag4)
is equivalent to
(flag2 && !flag4) || (!flag2 && flag4);
Map<String, Integer> ret = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
for (int key : map.keySet()){
ret.put(map.get(key),key);
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
list.add(i);
list.get(i);
}
add(value), add(index, value)
set(index. value)
clear()
indexOf(value)
lastIndexOf()
toString(), toArray();
Map<String, Integer> ret = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
for (int key : map.keySet()){
ret.put(map.get(key),key);
Understanding Networking and Server Visualization
Introduction to Virtualization
Virtualization and Cloud Computing are not same. Its a component of Cloud Computing.
In virtualization there is a separation of OS with the underlying H/W where as in Cloud Computing (CC), there is a separation of Application from the underlying hardware.
Type 1 Hypervisor (Native or Bare Metal) : A physical machine, and hypervisor on it.
Type 2 Hosted hypervisor : Comp. with an OS, and onto that hypervisor is installed eg :VMWare (installed according to the OS). Onto it guest OS are installed
Hosted solutions (Proprietary ones) on Amazon Cloud etc.
you need a management console to interact with hypervisor(once the physical server has an IP address). With the management console, you can move the instances of OS’s among different physical servers.
Also, according to resource needs, management console can migrate (or turn on and off) based on loads (balances the electricity consumption)
If the physical hardware running the hypervisor fails, management console can quickly migrate the OS to another hardware.
Over Allocation : static (RAM is split between all the OS instances) and
dynamic (logical allocation more than the physical)
Most of the hypervisor software are free (most of them based on XEN) but they charge for the management console software.
Careful with type 2 Hypervisor : Be careful of the resource allocation. if 4 GB’s of RAM is allocated, the type 2 virtualization hypervisor will take all 4 GB and allocate to the VM even if its not needed. Can crash host OS by overallocating its hardware resources.
Modifiers in java : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1MmietzIteA&list=PLYPjPMiw3_YsVockWfuuhoP86YPDUXp4f&index=4
Anything can be declared inside anything!!
Interface vs Abstract vs Concrete class
Class MySystem{
static string out = “nitin”;
}
MySystem.out.length(); //Compare it to
System.out.println(out);
JVM {
public static void nitin(String[] a)
}
*** In overloading check only method name (same) and argument type (different, at least order). Return types, access modifiers are not required.
**** In overriding: EVERYTHING should be same.
*** Both occur at runtime.