Echinoderms
Author Mia Yockey
Co-author Lila Boudrie
How we identified the organism:
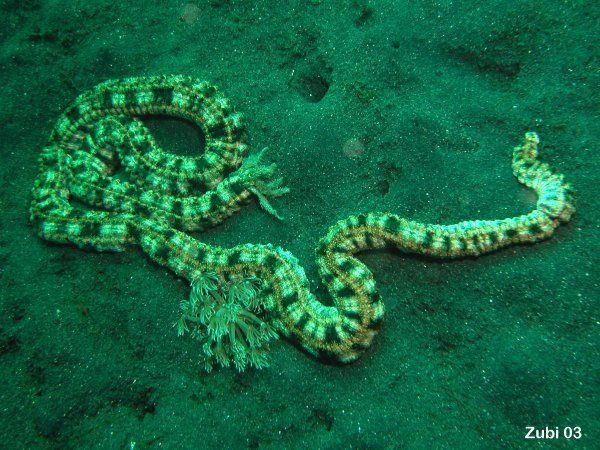
Boy, did we have fun figuring out this organism! At first we thought it would be in a phylum that had worm like features but we were pretty off. The organism wasn’t even a worm, it’s a type of sea cucumber. The Spotted snake sea cucumber to be exact , from the echinoderm phylum. The main give away was the suckers on the lower half of its body. Since that is a common trait of that phylum. It’s a relative to the starfish, the sea star, sand dollars, sea urchins and other sea cucumbers and many others. This phylum has a large variety of organisms contained in it.
The spotted snake sea cucumber ( the unknown organism), I wanted to use this image to show what it looked like (From pintrest) https://www.pinterest.com/pin/572168327629391493/
The rest of the phylum (similarities and differences):
A trait that all of the phylum share are the tentacles/ suckers on the bottom of the organisms,used for movement. Now lets move on to the traits of each class in the phylum, There are five total.
Crinoidea- This group contains sea lilies . They are the most primitive class in the phylum, having five or more arms.
Asteroidea- This group contains sea stars. They live on the ocean floor, they are either scavengers or predators. They are also brightly colored.
Ophiuroidea- They have a disc-shaped center, connected to the arms. They live in shallow or deep water. They are predatory, filter feeders and herbivores.
Echinoidea- This class contains the sea urchin and the sand dollar. They don’t have arms but they do have tube feet. As well as a specified mouth for eating food off the bottom of the sea floor.
Holothuroidea- The class of the sea cucumber the most bizarre of its phylum. They have along form, a respiratory system unlike the rest of its phylum, no arms. They live in deep water and are filter feeders or deposit feeders (they eat dead things).
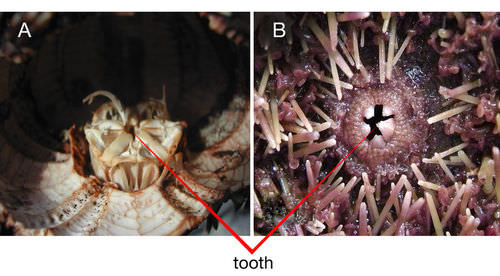 https://www.ck12.org/biology/types-of-echinoderms/lesson/Echinoderm-Classification-Advanced-BIO-ADV/
https://www.ck12.org/biology/types-of-echinoderms/lesson/Echinoderm-Classification-Advanced-BIO-ADV/
The mouth of sand dollar (left) and the mouth of sea urchin (right). This is a unique trait to only sea urchins and sea dollars, so I included it in my differences. (From ck12)
Services:
I am sure we can all look back at when we were a kid at the zoo and remember the touch tank. The small area that allowed you to touch some weird yet amazing creatures. This is a really good service because it’s a smart way to introduce people to Marine life, as well as teach kids and their parents about life in the Ocean and how to help them out. Possibly influencing the start of someones Marine biology (or any kind of science really) career. Plus any help to support the Ocean is always a great thing to see nowadays. Plus learning new knowledge is always a huge benefit for us in my opinion.
This phylum is also used for medicinal purposes, specifically the sea sponge. Since some of them are toxic ,their toxins have been to shown to slow down the growth of tumors,so research is done to see if they could be beneficial to cancer research. Some of the vitamins in sea cucumbers have also been used for noninflammatory and anti-microbial medicines.
Another benefit though for the organisms themselves it isn’t much of a benefit. Many members of this phylum are used as food, especially in Asia. Sea cucumbers are used to make a jello like stew that is considered a delicacy. Sad fact : Each year about 50,000 sea urchins and sea cucumbers are caught each year just for consumption alone,that’s pretty awful (So it’s a service for us but a huge disservice for the phylum) .
http://ourtravelingtribe.com/2014/12/oregon-coast-aquarium-newport.html
Image of a touch pool at the Oregon aquarium, since this was a part of my services I used an image of a touch tank (From the Oregon Coast Aquarium)
Disservices:
Because sea cucumbers are in such high demand, causing a black market , this causes the prices of this species to sky rocket, causing economical issues. Not only that but it means that these organisms are under the radar,which could mean big issues in the numbers of sea sponges. So it’s a big political, economical and environmental issue.
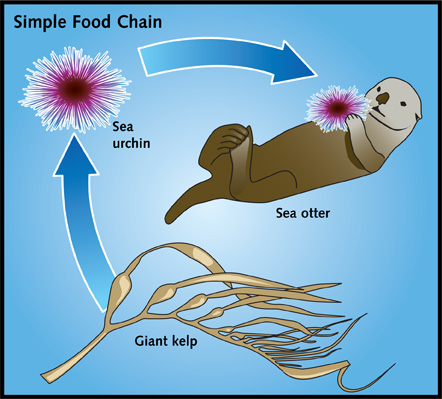
Another ecological issues is the relationship of Sea otters, sea urchins and kelp. Sea otters are a keystone species because their main food source is sea urchins, a sea urchins in turn eat kelp. So if sea otters become endangered, then the sea urchin numbers will skyrocket. Sea urchins will consume a lot of kelp and kelp makes kelp forests which is an important ecosystem for a large amount of species. So losing kelp due to over eating, can lead to the extinction of a lot of species who call kelp forests their home. How this effects, is due to a large number of species living in kelp forests. There are some that are fished by fishing industries and if they’re gone that could greatly impact the economy as much as the ecosystem. Sea urchins and sea otters are keystone species, meaning they can greatly change the environment they live in. This is important to humans a large variety of species we hunt will be destroyed if the kelp forests are gone. Many fish we catch make their homes here, even some sharks as well plus sea urchins as well. They will die out too if they’re main food source is gone, meaning we humans will be losing a lot of food resources. This would be a big issue for humans and animals because an ecosystem is gone and some parts of the world like Europe and Asia, consume a lot of seafood. Though sea food consumption happens everywhere.
http://science.jrank.org/kids/pages/58/OTTERS-URCHINS-KELP.html
This image is sued to convey the food web of the sea urchin and sea otter. Showing what eats what, a clarifying the relationship.
Cites:
https://www.ck12.org/book/CK-12-Life-Science-Concepts-For-Middle-School/section/9.12/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4446612/
https://ww2.kqed.org/quest/2014/02/25/balancing-act-otters-urchins-and-kelp/
https://www.ck12.org/biology/types-of-echinoderms/lesson/Echinoderm-Classification-Advanced-BIO-ADV/