Dump hydraulic pumps play a pivotal role in numerous industries, providing the necessary power for hydraulic systems to function efficiently. These pumps are specifically designed to handle heavy loads and are widely utilized in applications such as dump trucks and hydraulic cranes. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of dump hydraulic pumps, exploring their components, operating mechanisms, flow control, maintenance, and more. By understanding the inner workings of these pumps, we can appreciate their significance and ensure optimal performance in diverse industrial settings. Let’s embark on this journey to discover the world of dump hydraulic pumps together.
Overview of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic pumps serve as the heart of hydraulic systems, generating the necessary fluid power to operate various machinery and equipment. These pumps utilize mechanical force to convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, facilitating the movement of fluids and enabling the system to perform work.

There are different types of hydraulic pumps available, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Three common types are gear pumps, piston pumps, and vane pumps. Gear pumps are simple and cost-effective, suitable for low-pressure applications. Piston pumps offer high efficiency and are capable of handling high pressures. Vane pumps are known for their quiet operation and smooth flow delivery.
Now, let’s compare dump hydraulic pumps with other types. Dump hydraulic pumps are specifically designed for heavy-duty applications, such as lifting and dumping loads. They provide robust power and reliability, making them indispensable in industries where large-scale material handling is required. The distinctive features of dump hydraulic pumps make them a preferred choice for dump trucks, hydraulic cranes, and similar machinery.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the components, operating mechanisms, flow control, maintenance, and application areas of dump hydraulic pumps. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these pumps and their vital role in various industries.
Components of Dump Hydraulic Pumps
To comprehend the inner workings of dump hydraulic pumps, it is essential to familiarize ourselves with their main components. These components work in harmony to ensure the efficient and reliable operation of the pump. Let’s explore them in detail:
- Pump Housing: The pump housing serves as the outer casing that houses the internal components of the hydraulic pump. It provides structural support and protects the pump’s internal mechanisms.
- Impeller: The impeller is a rotating component within the pump that is responsible for creating suction and generating fluid flow. It uses centrifugal force to draw in hydraulic fluid and propel it through the system.
- Inlet/Outlet Ports: The inlet port is the entry point through which hydraulic fluid enters the pump, while the outlet port is the exit point for the pressurized fluid. These ports allow for the proper flow and circulation of the hydraulic fluid within the system.
- Seals: Seals are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the hydraulic pump. They prevent leakage and ensure that the fluid remains contained within the pump and its associated components. Common types of seals used in dump hydraulic pumps include O-rings, gaskets, and lip seals.
- Bearings: Bearings are used to support the rotating components of the pump, such as the impeller and shaft. They reduce friction and enable smooth operation, allowing the pump to operate efficiently and extend its lifespan.
- Other Essential Parts: Dump hydraulic pumps may also include additional components such as couplings, drive shafts, and mounting brackets. These parts contribute to the overall functionality and performance of the pump.
Understanding the role and interplay of these components is crucial for diagnosing issues, conducting maintenance, and optimizing the performance of dump hydraulic pumps. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the operating mechanisms, flow control, maintenance, and application areas of these pumps in greater detail.
Operating Mechanisms of Dump Hydraulic Pumps
Dump hydraulic pumps operate based on fundamental principles that enable them to generate hydraulic power. Understanding these mechanisms is key to comprehending how dump hydraulic pumps function. Let’s delve into the operating mechanisms of these pumps:
- Suction: The pump’s operating cycle begins with the suction phase. During this phase, the rotating impeller creates a low-pressure zone within the pump housing. This low-pressure zone allows hydraulic fluid to be drawn into the pump from the reservoir or hydraulic tank.
- Compression: Once the hydraulic fluid enters the pump through the inlet port, the impeller’s rotation forces the fluid towards the outlet port. As the fluid moves towards the outlet, it undergoes compression. The impeller’s design and rotation create a high-pressure zone, increasing the fluid’s pressure.
- Discharge: The compressed hydraulic fluid is then discharged from the pump through the outlet port. It exits the pump under high pressure, ready to be utilized in various hydraulic applications.
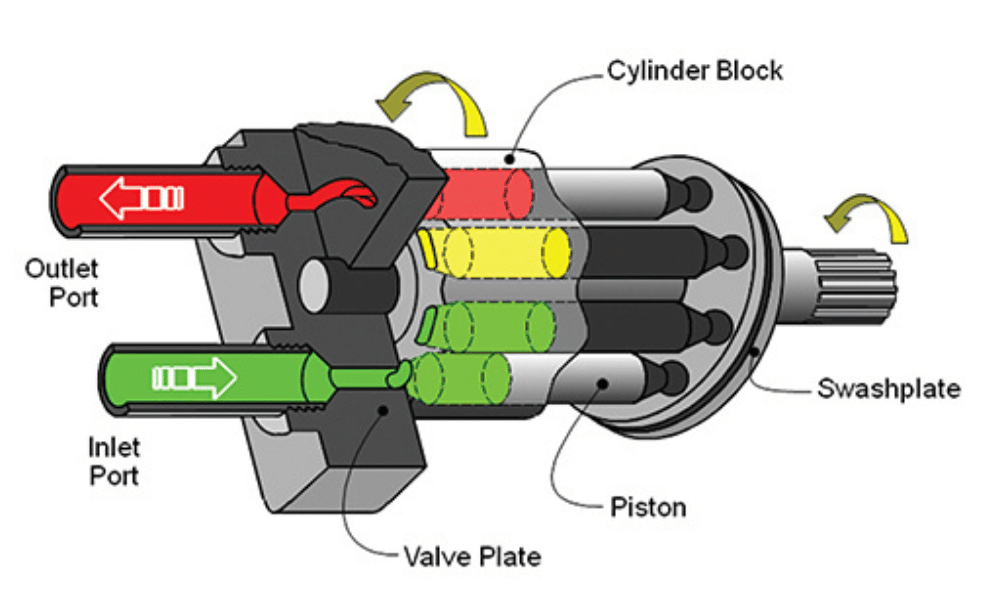
The movement of hydraulic fluid within dump hydraulic pumps is facilitated by pistons, gears, or vanes, depending on the pump type. These components play a vital role in generating fluid flow and ensuring the efficient transfer of hydraulic energy.
Piston pumps utilize reciprocating pistons to create pressure differentials, drawing in and discharging hydraulic fluid. They are well-suited for high-pressure applications and provide precise control over fluid flow.
Gear pumps employ interlocking gears to generate fluid flow. As the gears rotate, they trap and transport the hydraulic fluid, effectively transferring energy and pressurizing the fluid.
Vane pumps utilize rotating vanes within a cylindrical cavity. The vanes slide in and out of slots, generating fluid flow and pressurizing the hydraulic fluid.
By comprehending these operating mechanisms, we can gain a deeper understanding of how dump hydraulic pumps convert mechanical energy into hydraulic power. In the subsequent sections, we will explore flow control, pressure regulation, efficiency considerations, and other essential aspects of these pumps.
Flow Control and Pressure Regulation
Flow control and pressure regulation are crucial aspects of dump hydraulic pumps to ensure optimal performance and system safety. Let’s delve into the importance of flow control, the role of control valves and relief valves, and how pressure adjustments and flow rate optimization are achieved.
- Importance of Flow Control: Flow control is essential for managing the rate of hydraulic fluid flow within the system. It allows for precise control over the speed and movement of actuators, ensuring smooth and controlled operation. By regulating flow, operators can enhance the efficiency, safety, and performance of hydraulic equipment.
- Control Valves: Control valves play a central role in flow control. They are responsible for directing and adjusting the flow of hydraulic fluid. These valves can be manually operated or automated, allowing for precise control over the flow rate. By adjusting the position of the valve, operators can increase or decrease the flow of hydraulic fluid, thereby controlling the speed and force exerted by actuators.
- Relief Valves: Relief valves are essential for pressure regulation and system safety. They protect hydraulic systems from excessive pressure by opening and allowing fluid to bypass when pressure exceeds a predetermined limit. This prevents damage to the system and its components. Relief valves can be set to specific pressure limits and are designed to automatically reset once the pressure returns to a safe range.
- Pressure Adjustments and Flow Rate Optimization: Dump hydraulic pumps often require adjustments to suit the specific requirements of the application. Pressure adjustments can be made by regulating the relief valve setting or adjusting the control valve positions. This allows operators to fine-tune the system’s pressure levels and optimize its performance.
Flow rate optimization involves finding the right balance between fluid flow and actuator speed. By adjusting the control valve opening, operators can achieve the desired flow rate that matches the operational needs of the hydraulic equipment. Proper flow rate optimization ensures efficient power delivery and prevents excessive fluid consumption.
By effectively controlling flow and regulating pressure, dump hydraulic pumps can operate at their optimum capacity, maximizing performance and ensuring the longevity of the hydraulic system. In the subsequent sections, we will explore efficiency and performance considerations, maintenance, troubleshooting, and application areas of dump hydraulic pumps.
Efficiency and Performance Considerations
Efficiency and performance are key considerations when it comes to dump hydraulic pumps. Optimizing these factors ensures reliable operation, minimizes energy consumption, and maximizes the overall productivity of hydraulic systems. Let’s explore the factors that influence the efficiency and performance of dump hydraulic pumps:
- Pump Efficiency: Pump efficiency is a measure of how effectively the pump converts mechanical power into hydraulic power. Higher efficiency means less energy loss during the conversion process. Factors that affect pump efficiency include design, internal friction, and clearances. Choosing a pump with high efficiency can result in reduced power consumption and improved overall system performance.
- Power Consumption: Dump hydraulic pumps consume power to operate and generate hydraulic energy. It is important to select a pump that matches the power requirements of the hydraulic system. An oversized pump can lead to unnecessary power consumption, while an undersized pump may result in insufficient power delivery. Proper sizing and selection of the pump are crucial for achieving optimal power consumption.
- Heat Generation: Hydraulic systems can generate significant heat during operation. Excessive heat can degrade the performance of the pump and other system components. To maintain optimal performance, it is important to manage heat effectively through proper cooling methods, such as heat exchangers or temperature control devices. This helps to prevent overheating and ensures the longevity of the pump and system.
- Proper Sizing and Selection: Selecting the right size and type of dump hydraulic pump is essential for optimal performance. Factors such as flow rate, pressure requirements, and duty cycle should be considered when choosing a pump. Proper sizing and selection ensure that the pump operates within its designed parameters, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced wear and tear, and enhanced overall system performance.
- System Optimization: The overall design and configuration of the hydraulic system can also impact the efficiency and performance of the dump hydraulic pump. Proper system layout, appropriate use of valves and actuators, and effective routing of hydraulic lines contribute to optimal performance. Additionally, regular system inspections and maintenance help identify and address any inefficiencies or performance issues.
By considering these efficiency and performance factors, operators and engineers can optimize the operation of dump hydraulic pumps, resulting in improved productivity, reduced energy consumption, and extended equipment lifespan. In the following sections, we will explore maintenance and troubleshooting practices for dump hydraulic pumps, as well as their application areas in various industries.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are vital for the reliable and efficient operation of dump hydraulic pumps. Regular maintenance helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, extends the lifespan of the pump, and ensures optimal performance. Let’s explore the importance of maintenance and common troubleshooting practices for dump hydraulic pumps:
- Importance of Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity and performance of dump hydraulic pumps. It involves a series of preventive measures to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. Routine maintenance tasks include:
- Fluid Checks: Regularly inspect the hydraulic fluid level and quality. Ensure that the fluid is at the recommended level and free from contamination. Contaminated or degraded fluid should be replaced promptly.
- Filter Replacements: Hydraulic filters prevent debris and contaminants from entering the pump and system. Regularly inspect and replace filters as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain optimal pump performance.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of moving parts, such as bearings and gears, is essential for reducing friction and ensuring smooth operation. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication intervals and use the recommended lubricants.
- Visual Inspections: Conduct visual inspections of the pump housing, seals, fittings, and other components. Look for signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage and ensure the pump’s reliability.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: Despite regular maintenance, dump hydraulic pumps may encounter occasional issues. Understanding common problems and their potential causes can aid in troubleshooting. Some common pump issues include:
- Leaks: Leaks can occur at various points within the pump, such as seals, fittings, or connections. Inspect for visible leaks and address them promptly. Ensure proper sealing and tight connections.
- Decreased Performance: If the pump’s performance is compromised, it could indicate issues such as worn-out components, reduced fluid levels, or clogged filters. Conduct a thorough inspection to identify the root cause and take appropriate corrective actions.
- Unusual Noises: Unusual noises, such as grinding or whining sounds, may indicate problems within the pump or associated components. Inspect for loose parts, damaged bearings, or misaligned components.
- Overheating: Excessive heat generation can affect pump performance. Check for proper cooling, ensure adequate fluid levels, and inspect the pump for any obstructions or restrictions in fluid flow.
By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and promptly addressing any troubleshooting issues, operators can ensure the reliable and efficient performance of dump hydraulic pumps. In the subsequent section, we will explore the application areas and industries where dump hydraulic pumps are commonly utilized.
Application Areas and Industries
Dump hydraulic pumps find extensive application in various industries where robust power and efficient material handling are required. Let’s explore some of the key application areas and industries where dump hydraulic pumps are commonly utilized:
- Dump Trucks: Dump trucks heavily rely on hydraulic systems equipped with dump hydraulic pumps. These pumps provide the necessary power to raise and lower the truck’s bed, allowing for efficient loading and unloading of materials at construction sites, mining operations, and waste management facilities.
- Hydraulic Cranes: Hydraulic cranes utilize dump hydraulic pumps to lift and maneuver heavy loads with precision. These pumps enable the smooth operation of the crane’s boom, jib, and other hydraulic components, making them indispensable in construction, infrastructure development, and logistics industries.
- Construction Equipment: Dump hydraulic pumps are extensively used in various construction equipment, including loaders, excavators, bulldozers, and compactors. These pumps provide the power needed for lifting, digging, pushing, and compacting operations, enhancing the efficiency and productivity of construction projects.
- Agricultural Machinery: Dump hydraulic pumps are employed in agricultural machinery, such as harvesters, tractors, and sprayers. These pumps assist in hydraulic steering, implement control, and other vital functions, contributing to the smooth operation and productivity of agricultural operations.
- Material Handling Equipment: Dump hydraulic pumps play a vital role in material handling equipment, such as forklifts, pallet jacks, and conveyor systems. These pumps enable the lifting, lowering, and movement of heavy loads, facilitating efficient warehouse operations and logistics.
- Mining and Quarrying: Dump hydraulic pumps are extensively utilized in the mining and quarrying industry. They power hydraulic systems in mining equipment, including loaders, excavators, and haul trucks, enabling the extraction and transportation of minerals and materials.
- Waste Management: Dump hydraulic pumps are crucial in waste management applications, such as garbage trucks and waste compactors. These pumps enable the efficient collection, transportation, and compaction of waste materials, contributing to effective waste management practices.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Machinery: Dump hydraulic pumps find applications in manufacturing and industrial machinery, including hydraulic presses, machine tools, and automation systems. These pumps provide the necessary power for precise movement, control, and operation of equipment in various manufacturing processes.
The versatility and adaptability of dump hydraulic pumps make them an integral component in a wide range of industries, where heavy lifting, material handling, and precise control are essential. In the final section, we will recap the inner workings of dump hydraulic pumps and emphasize their significance in various industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dump hydraulic pumps play a vital role in numerous industries, providing the necessary power for hydraulic systems to efficiently handle heavy loads and perform various tasks. We have explored the components, operating mechanisms, flow control, maintenance, troubleshooting, and application areas of dump hydraulic pumps throughout this guide.
By understanding the inner workings of dump hydraulic pumps, including their main components such as pump housing, impeller, and inlet/outlet ports, as well as their working principles of suction, compression, and discharge, operators and engineers can optimize the performance and reliability of these pumps.
We have also highlighted the importance of flow control, pressure regulation, efficiency considerations, and regular maintenance for dump hydraulic pumps. Proper flow control and pressure regulation ensure smooth operation and system safety, while maintenance practices such as fluid checks, filter replacements, and visual inspections help prevent issues and maintain optimal performance.
Dump hydraulic pumps find application in a wide range of industries, including dump trucks, hydraulic cranes, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and waste management. Their versatility, robust power, and adaptability make them indispensable for material handling, lifting, and precise control in these industries.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of dump hydraulic pumps, their components, mechanisms, and application areas, operators and engineers can ensure the efficient operation of hydraulic systems, maximize productivity, and contribute to the success of various industries.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights into dump hydraulic pumps and their crucial role in powering hydraulic systems across diverse sectors.
Related Keywords
# Dump Trailer Hydraulic Cylinder,
# Heavy Duty 12 Volt Hydraulic Pump,
# 12V Double Acting Hydraulic Pump,
# Hydraulic Pump for Dump Trailer near me,
# 12V Hydraulic Pump and Ram,
# KTI Hydraulic Pump Manual,

